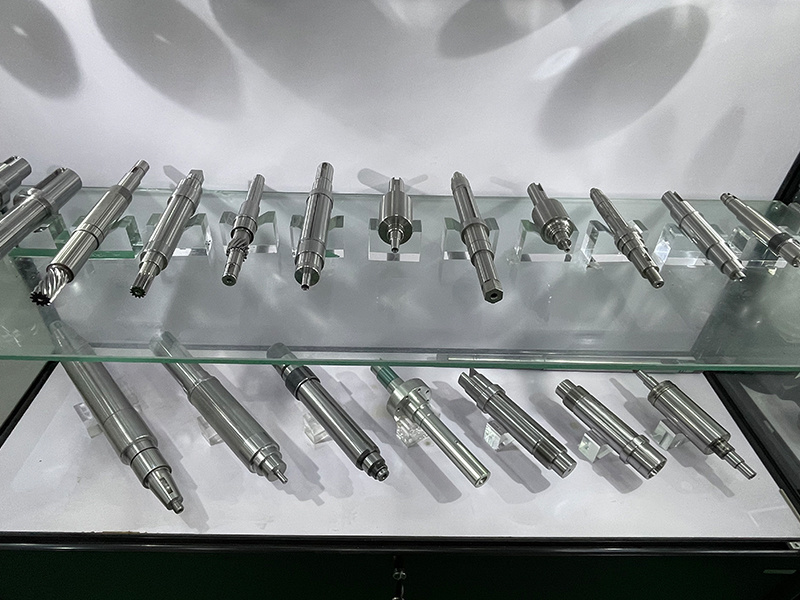
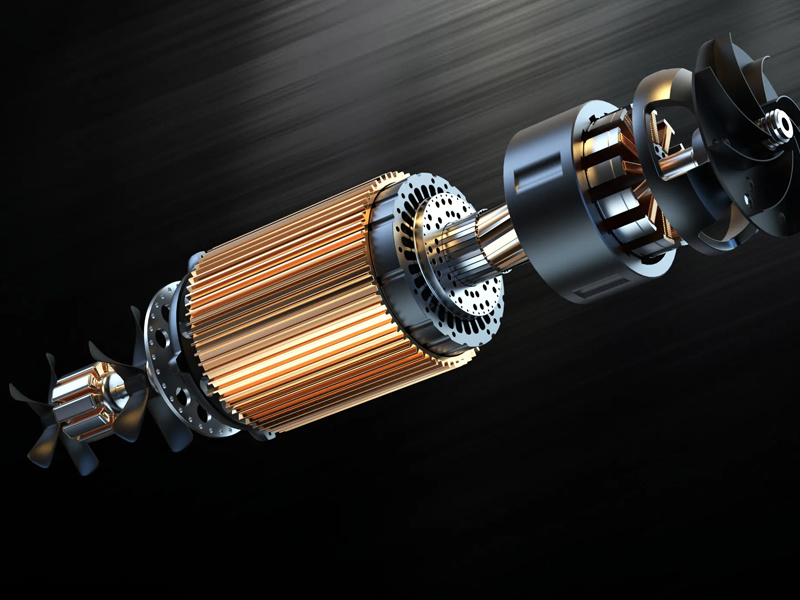
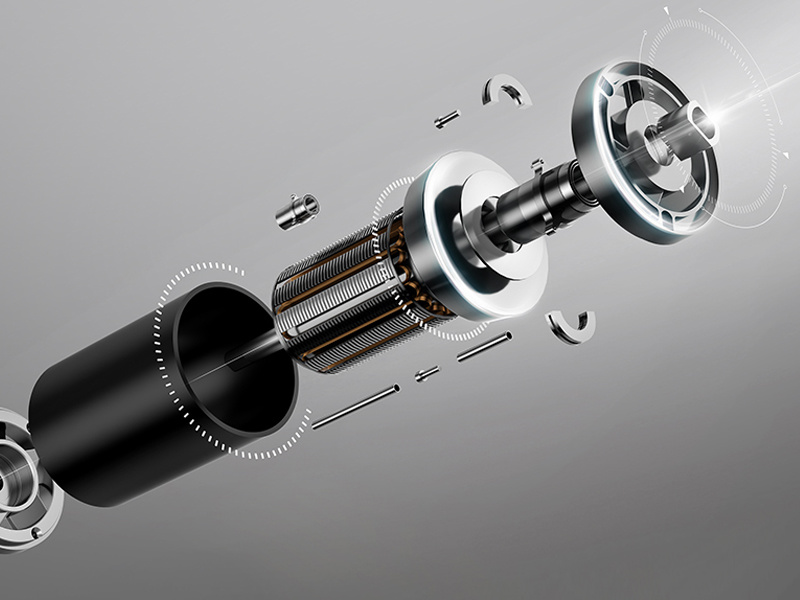
What are the common types of motor shafts?
Release time:
2021-06-30
The shaft is an important component in a motor, serving as the link for electromechanical energy conversion between the motor and the equipment.
The shaft is an important component in a motor, serving as the link for electromechanical energy conversion between the motor and the equipment, supporting rotating parts, transmitting torque, and determining the relative position of rotating parts to the stator. Therefore, the motor shaft must have reliable strength and rigidity to ensure the realization of the preset design functions. The following briefly describes various types of motor shafts and their characteristics, providing references for the selection and design of motor shafts.
Types of Shafts and Their Applicability
● Classified by the presence or absence of steps on the shaft. It can be divided into smooth shafts and stepped shafts. Smooth shafts are often made of cold-drawn round steel, which can reduce the processing time for the outer diameter of the shaft and are sometimes used in micro motors. Stepped shafts can conveniently and reliably accommodate many different components, so most motors use this type of shaft.
In stepped shafts, they can be further divided into unidirectional stepped shafts (where the stepped diameter decreases gradually from one end of the shaft to the other) and bidirectional stepped shafts (where the stepped diameter decreases gradually from the middle of the shaft to both ends).
● Classified by the manufacturing method of the shaft blank. It can be divided into round steel shafts (shafts made from hot-rolled round steel), forged shafts (shafts made from forgings), and welded shafts (shafts with radial ribs welded on).
Shafts made from hot-rolled round steel are common in medium and small motors. The material of the shaft is often 45 carbon structural steel. For small power motors, some use Q235 ordinary carbon steel. The blank diameter must be selected based on the shaft diameter plus the processing allowance. Therefore, the cutting volume is relatively large.
Shafts with a diameter of over 100 millimeters should use forged shafts. Forged steel has higher mechanical strength, and forging the approximate shape of the stepped shaft can save raw materials and cutting time. For large shafts with high mechanical strength requirements, such as turbine generator shafts, alloy steel is commonly used for forging.
Welded shafts replace the rotor support with radial ribs, which can increase the ventilation area of the rotor cavity. However, when welding ribs, it is easy to cause deformation of the shaft, and post-welding annealing treatment is required. During machining on a machine tool, the cutting is not continuous, which is unfavorable for the tools. Due to the presence of welds, the fatigue strength of the shaft is significantly reduced, making it unsuitable for high-speed motors.
● Classified by the method of combining the shaft with the core. It can be divided into knurled shafts in the middle, heat-shrinkable shafts, and shafts with keyways in the middle. Knurled shafts are used for small motors under 10 kilowatts, saving the work of processing keys and keyways. However, when pressing the shaft into the core, it is easy to cause deformation of the shaft. During motor operation, some rotor cores with knurled connections exhibit axial movement. This deformation of the shaft is caused by the tight fit between the core and the shaft, while the axial displacement is due to insufficient interference fit between the two.
Heat-shrinkable shafts do not have knurling or keyways in the middle. There is a certain amount of interference between the shaft and the inner hole of the core, allowing the shaft to be fitted into the core while it is hot. As long as the interference is chosen appropriately, the combination of the rotor core and the shaft is very reliable.
Shafts with keyways in the middle can be further divided into those with one keyway and those with two keyways. Shafts with one keyway are used for small motors, while those with two keyways are used for medium and large motors. The rotor core (or support) is combined with the shaft using keys. The core is axially fixed, with one end using a shoulder and the other end using an arc-shaped key locked in the annular keyway on the shaft. This type of shaft can transmit larger torque and is often used in high-power motors and motors that frequently reverse or where the rotor core should not be heat-shrinkable.
● Classified by the shape of the shaft extension. It can be divided into cylindrical shaft extensions, conical shaft extensions, and shaft extensions with half couplings. Cylindrical shaft extensions are easy to process and are widely used in motors. Conical shaft extensions have fastening bolts and require more processing. However, the drive wheels mounted on them are easy to install and remove, making them commonly used in special motors. Shafts with half couplings are mainly used in hydraulic turbines and large DC motors.
● Classified by the shape of the shaft core. It can be divided into solid shafts, shafts with deep holes at one end, and shafts with a central through hole. Solid shafts are commonly used in motors. Shafts with deep holes at one end are mainly used in wound asynchronous motors to connect the lead wires on the rotor through the hole to the collector ring outside the end cover. Shafts with a central through hole are mainly used in large motors: in double-water-cooled turbine generators, the central through hole also serves as part of the cooling water circuit.
● Classified by the magnetic conductivity of the shaft. It can be divided into conductive shafts and non-conductive shafts. Conductive shafts are mainly used in turbine generators. Other motor shafts usually do not require conductivity.
● Other classification methods. Depending on the number of shaft extensions, it can be divided into single shaft extension and double shaft extension; depending on the number of bearings, it can be divided into single bearing shafts, double bearing shafts, and multi-bearing shafts.
Related Blogs
What are the selection requirements for shaft machining processes?
The shaft is generally manufactured from rolled round steel or forged pieces through cutting processing.
The heat generation situation of losses in the main spindle motor of new energy vehicles.
The losses of the electric spindle motor generate heat. From the basic structure of the electric spindle, it can be seen that the motor is installed inside the electric spindle.
How to extend the lifespan of industrial motor shafts?
How can we increase the lifespan of industrial motor shafts? Especially, what are effective measures to prevent current issues in industrial motor shafts?